The balance sheet is a financial position and a part of a financial statement. It includes a business’s assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity. And that should be at a specific point in time. To prepare a balance sheet, you will first need the company’s specific point in time.
Then calculate its total assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity. Then put them in as per the accounting equation. The total amount of liabilities and owner’s equity should match the total amount of assets. We provided multiple downloadable balance sheet templates that will make you more clear about the format.
What Are the Components of a Balance Sheet in Bangladesh?
A balance sheet mainly has three components. Assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity. These components are again divided into different categories.
Current Assets
Current assets are short-term resources that can be converted to cash within 1 year or less. Some of its examples are
- Cash: It’s a company’s readily available funds, which include bank accounts, checks, and physical currency.
- Accounts receivable: This is the money that a business is owed from its customers for selling goods and services and hasn’t received the money yet.
- Inventory: This refers to the value of the company’s goods that it intends to sell. It should be sold within one year of the operating cycle to be converted into cash.
- Prepaid expense: It is the amount that a business pays in advance for buying any goods or services. And the company will benefit from it in the future.
Non-Current Assets
Non-current assets are long-term resources. They provide both monetary and economic benefits to the company for more than one year. Such assets include:
- Property: It is the long-term tangible asset. A company won’t intend to sell its property in its ordinary course of business.
- Plant & Equipment: This is also a long-time intangible asset that a business uses to generate revenue. They will be realized into cash in more than one year.
- Intangible Assets: It has value but lacks physical substance. Such as patent, trademark, goodwill, brand reputation, and copyright. They are not expected to be converted to cash within less than one year.
Current Liabilities
Current liabilities are financial obligations, like debts. A company must pay the dues within one year of its operating cycle. Some of the common current liabilities are
- Accounts Payable: It is like a short-term debt that a company owes to its suppliers for its goods and services. And those goods and services are purchased on credit. The company must pay it within one year or less.
- Short-term debt: This is also a debt obligation that a company owes and has to pay within 12 months of its operating cycle.
- Accrued expenses: These are the expenses that a company has to pay but has not paid yet. This can be rent, interest, or wages. The company must pay them within one year or less.
Non-Current Liabilities
Non-current liabilities are long-term financial obligations. They are like dues for the company that it will pay in more than one year. These are also called larger obligations, like
- Long-term loans: This includes long-term bank loans or debentures that are due for the business for more than one year.
- Deferred tax liabilities: It is a tax payment that a company has to pay within more than 12 months. Its date can be postponed sometimes.
- Bonds payable: It’s a long-term debt instrument. A company issues it to raise capital. Usually bonds payable are presented as dues for more than 1 year.
- Lease obligations: It’s a long-term financial commitment from the company to make lease payments. It can be for equipment or property, but that extends one year.
Owner’s Equity
Owner’s equity is the company’s or business’s value that its shareholders own. In short, it’s the shareholders’ residual interest that’s presented after deducting liabilities from assets.
- Paid-up capital: It is the company’s value that it has received from shareholders for the shares of its stock.
- Retained earnings: This is the accumulated profit of the company that has not been distributed as dividends. It’s also known as the saved money of the company that it intends to use for reinvesting in business or to distribute among shareholders.
- Reserve: This is also accumulated profits that a business sets aside for generating its financial strength or any specific purpose.
What’s the Difference Between Balance Sheets for Different Business Types in Bangladesh?
In Bangladesh, there are many types of businesses with different balance sheets. But the most common types are
Sole Proprietorships
Sole proprietorship is the easiest business structure. It is owned by one person only. And he operates it alone.
So, how does a sole proprietorship balance sheet differ? Since the owner and business are the same, the balance sheet doesn’t show wages or salaries for the owner. It just shows capital, assets, liabilities, and profit or loss. This type of balance sheet is often used for tax reporting only.
Partnership Businesses
Partnership businesses are formal agreements between two parties or more who agree to cooperate and combine resources. They can be individuals, businesses, interest-based organizations, or entities. The balance of partnership business includes each partner’s capital and drawings. It may also show profit-sharing ratios.
Private Limited Companies
A private limited company is a type of business entity or business structure. Here ownership is limited to certain numbers of shareholders. A private limited company doesn’t trade its shares publicly in a stock exchange. That’s why its entity is “private.” Balance sheets for private limited companies include share capital, retained earnings, director salaries, and sometimes dividends. In Bangladesh, private limited businesses often follow the formal structure of the balance sheet.
How to Prepare a Balance Sheet in Bangladesh: Step-by-Step Guide
Here are the steps of preparing a balance sheet that are commonly followed in Bangladesh.
Step 1: Identify Reporting Period (Monthly/Quarterly/Annually): In the balance sheet, the financial position is determined at a particular point in time. It can be at the end of the month, quarter, or fiscal year. But most commonly, it is prepared every 12 months. Such as the end of June or December.
Step 2: Gather Financial Data (Assets, Liabilities, Owner’s Equity): As per the ledger and trial balance, a balance sheet shows all permanent accounts. Permanent accounts are the entries that carry balances to the financial statements or over to the next period. These can be cash, fixed assets, etc. You need to identify those accounts and put in their balances.
Step 3: List & Subtotal All Assets: List all current and non-current assets from the trial balance. Such as accounts receivable, inventory, prepaid expenses, cash, fixed assets, and intangible assets. Add all of them and find the grand total assets.
Step 4: List & Subtotal All Liabilities: Now calculate the total liabilities. Make sure both current liabilities and non-current liabilities are recorded here. Now make a subtotal of them.
Step 5: Calculate Owner’s Equity: Shareholder’s or owner’s equity is the net worth of the company. Two types of investment are counted here. They are profits or losses accumulated by the business and capital contributed by the owners or shareholders.
Some of the common elements of owner’s equity are common stock, retained earnings, treasury stock, owner’s capital, etc. Calculate all of them and put the balance under liabilities’ balance.
Step 6: Verify That Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity: The universal accounting equation is,
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Equity
See if the total of liabilities and owner’s equity matches with total assets. If not, there must be errors in the listing or numbers. So double-check the lists and calculations.
Use Accounting Software Like Financfy
Using accounting software like Financfy helps you to prepare an accurate balance sheet. The software automates calculations and reduces the risk of human errors. Also, it can automatically update data, financial statements in real-time and ensure that your balance sheet follows standard accounting principles, like GAAP or IFRS.
Balance Sheet Format in Bangladesh
Here is a balance sheet example for a Bangladeshi company.
Balance Sheet
ABC Company
As of April 30, 2025
| Particulars | Taka | Taka |
|---|---|---|
| Assets | ||
| Current Assets: | ||
| Cash | ৳40,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | ৳70,000 | |
| Prepaid expenses | ৳30,000 | |
| Inventory | ৳50,000 | |
| Short-term investments | ৳30,000 | |
| Total Current Assets | ৳220,000 | |
| Long-term Assets: | ||
| Property, plant, and equipment | ৳100,000 | |
| Long-term investment | ৳150,000 | |
| Less: Accumulated depreciation | (৳40,000) | |
| Total Long-term Liabilities | ৳210,000 | |
| Total Assets | ৳430,000 | |
| Liabilities and Owner's Equity | ||
| Liabilities | ||
| Current Liabilities: | ||
| Accounts payable | ৳20,000 | |
| Short-term loans | ৳40,000 | |
| Unearned revenue | ৳30,000 | |
| Income tax payable | ৳20,000 | |
| Current portion of long-term debt | ৳60,000 | |
| Total Current Liabilities | ৳170,000 | |
| Long-term liabilities: | ||
| Deferred income tax | ৳40,000 | |
| Long-term debt | ৳60,000 | |
| Bank loan | ৳50,000 | |
| Total Long-term Liabilities | ৳150,000 | |
| Total Liabilities | ৳320,000 | |
| Owner's Equity | ||
| Owner's investment | ৳50,000 | |
| Retained earnings | ৳60,000 | |
| Total Owner's Equity | ৳110,000 | |
| Total Liabilities and Owner's Equity | ৳430,000 |
Download Balance Sheet Format in Bangladesh
Use the following formats and templates to prepare a balance sheet for your organization.
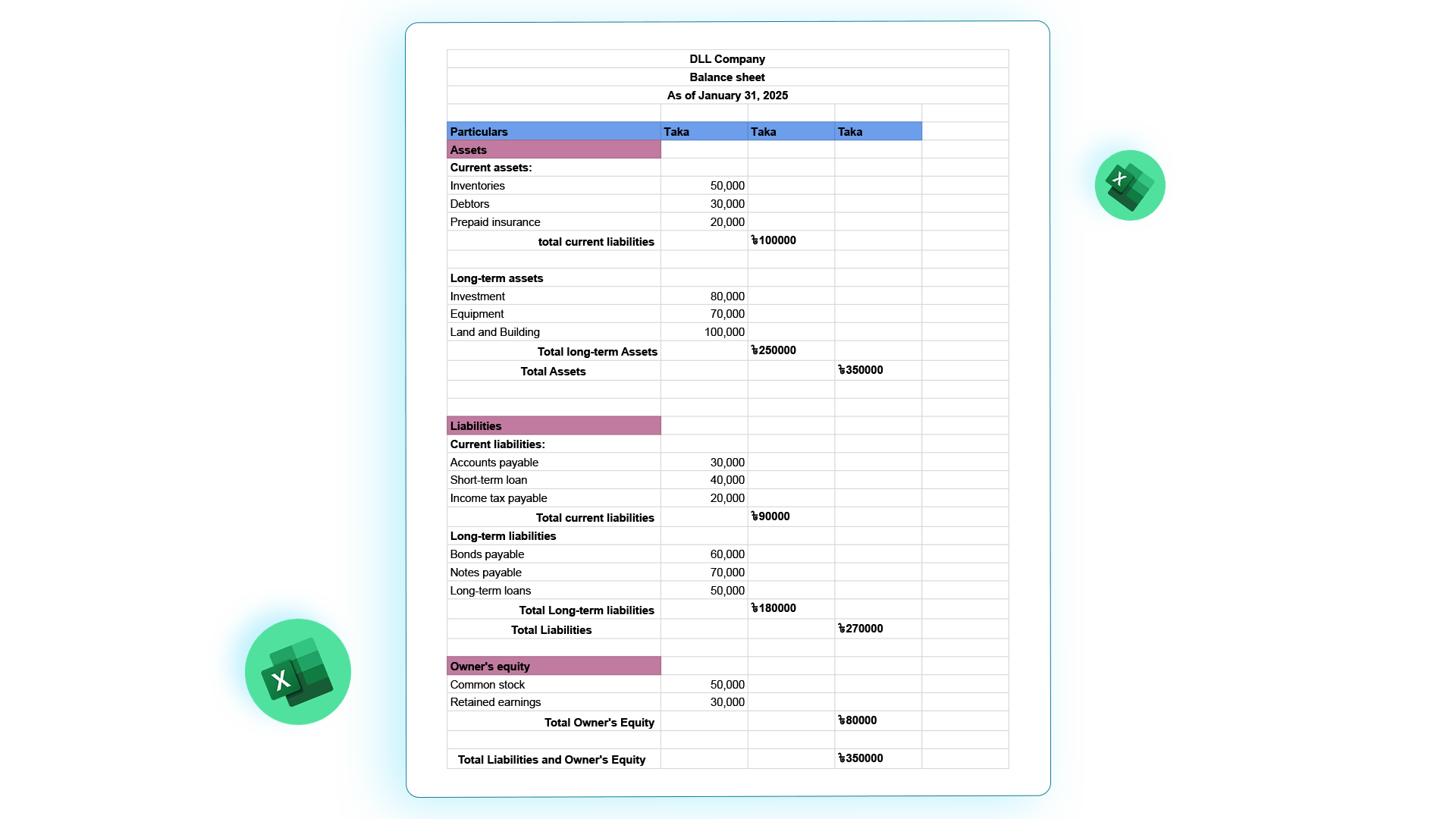
Balance Sheet Template in for Small Business (BD)
Follow this SME balance sheet format Bangladesh especially when you are running a small business.
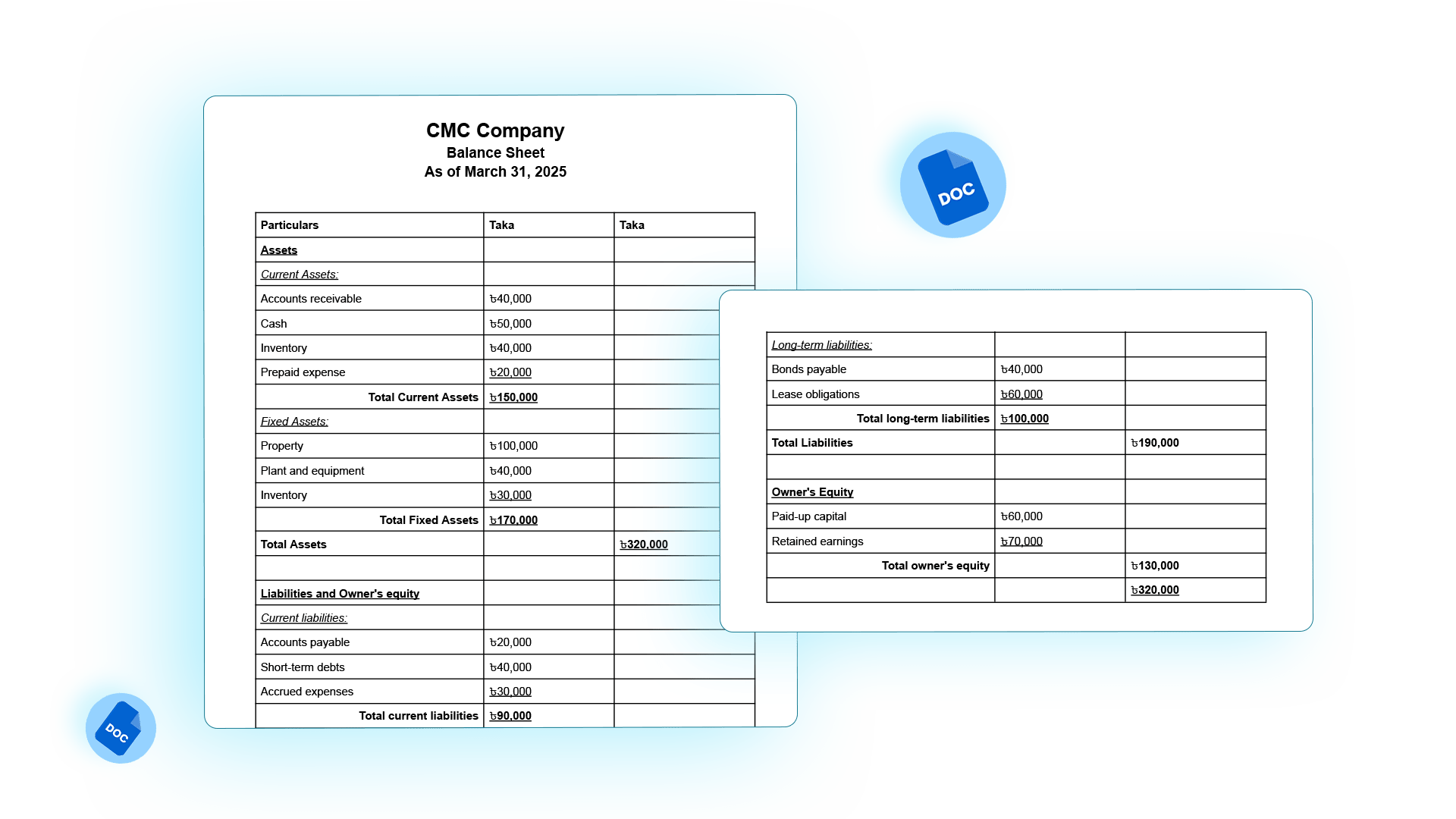
Audited Company Balance Sheet Template (RJSC ready)
Do follow this audited balance sheet format Bangladesh if your company is RJSC ready.
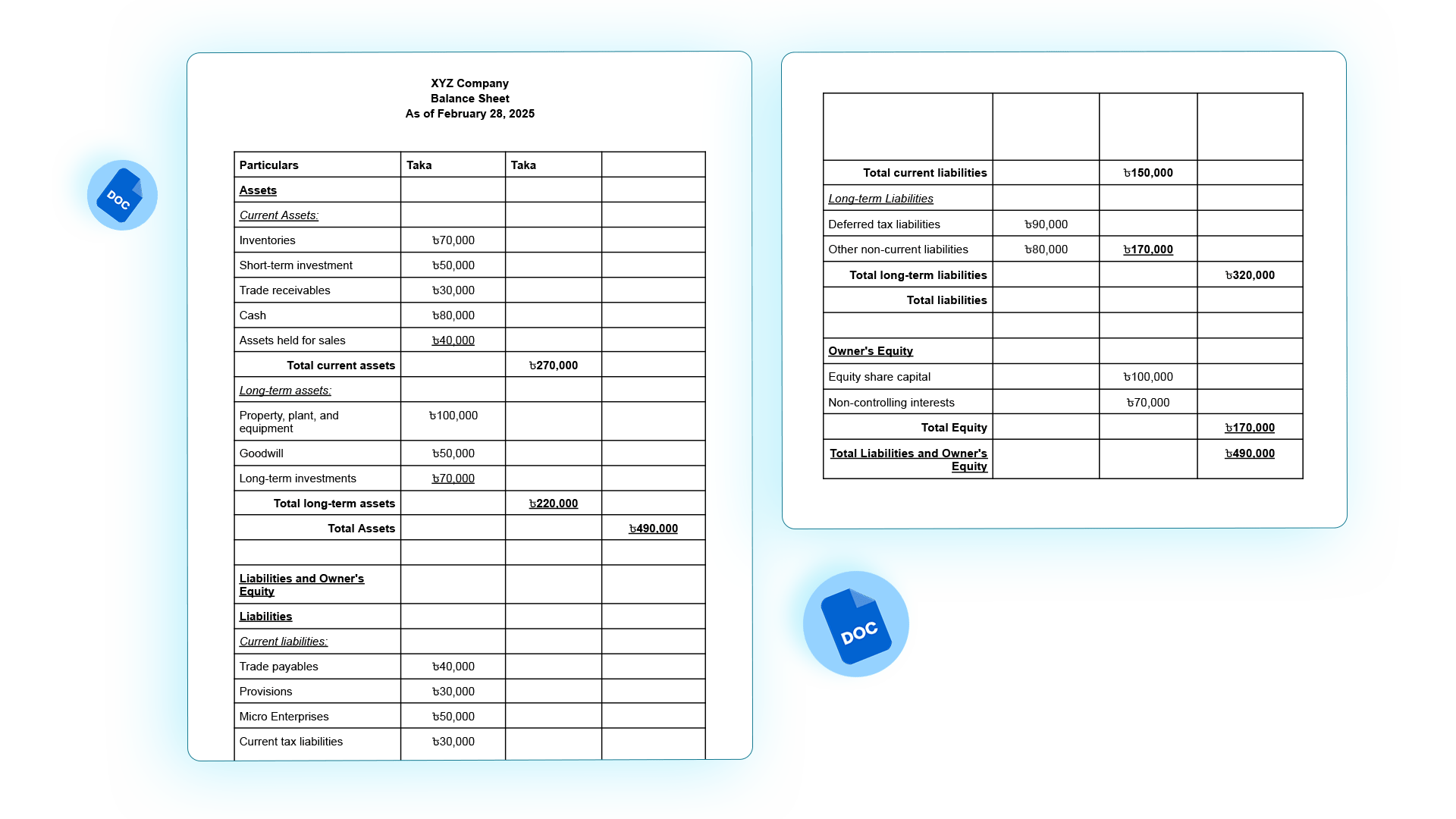
Balance Sheet Format in Excel for Loan/Investor Use
Here is an Excel balance sheet for Bangladeshi business.
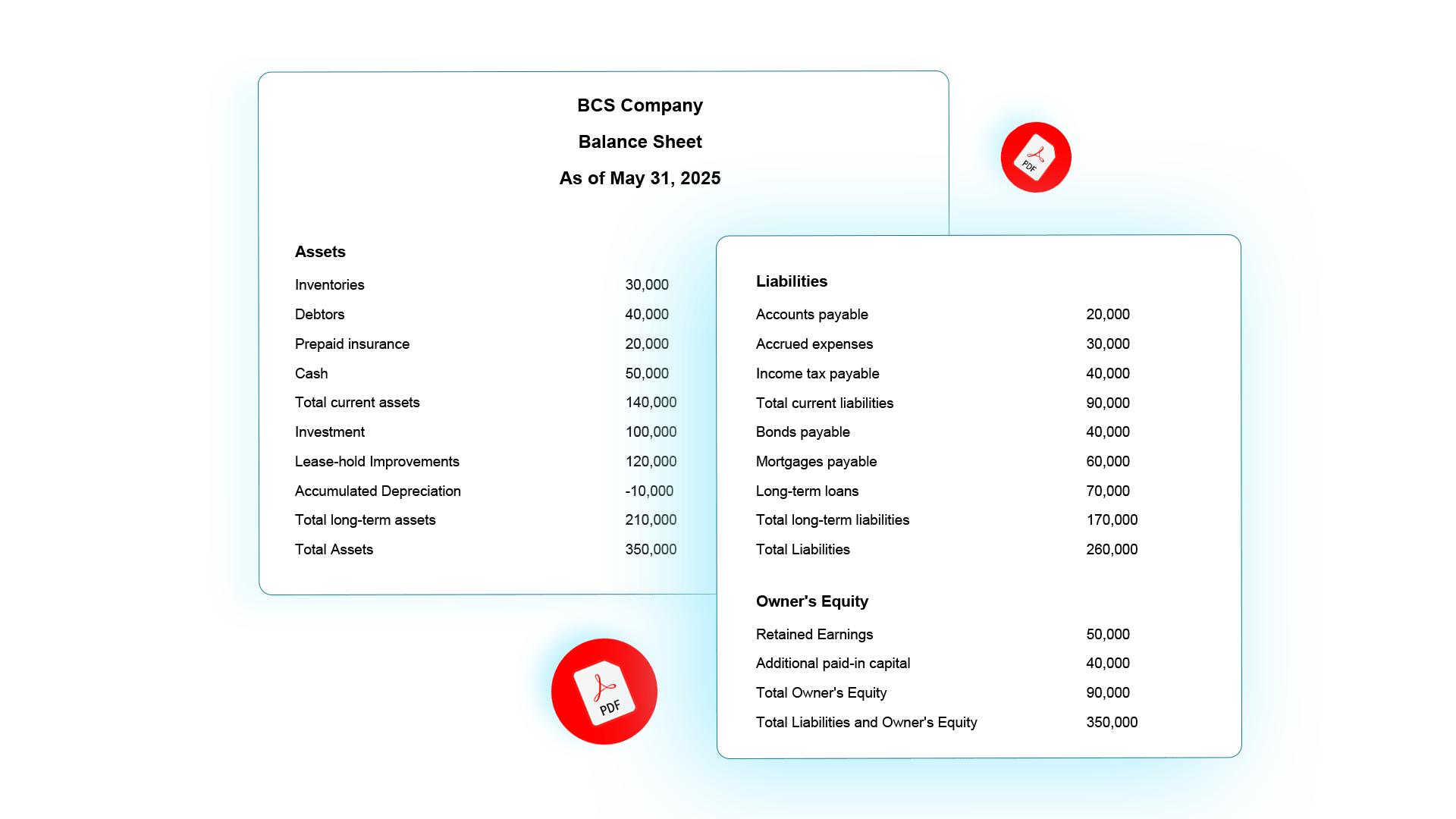
Classified Balance Sheet Format in PDF
Try out this free balance sheet template for your organization.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Bangladeshi Balance Sheet Format
Following are some common mistakes that occur while preparing a balance sheet. Be sure and avoid them while preparing one.
- Misclassification of assets/liabilities: Ambiguous transactions or manual data entry can sometimes lead to misclassification. That’s why you should review and reconcile the chart of accounts regularly
- Not balancing both sides: Unrecorded transactions, calculation errors, or missing entries can cause the balance sheet to not balance. For this, check the suspense account, recheck the opening balance, and calculate totals.
- Missing tax liabilities: Irregular tax filings or not recording accruals can make you miss the tax liabilities. You must reconcile with tax returns, file taxes regularly, and record accrued taxes even if they are unpaid.
- Ignoring depreciation: Sometimes incomplete bookkeeping or not maintaining a fixed assets register can result in ignoring depreciation. So maintain a fixed assets register, schedule regular depreciation entries, and review financial statements often.
Conclusion
The balance sheet format in Bangladesh follows the accounting equation, Assets = Owner’s Equity + Liabilities. If your balance sheet doesn’t match assets with the total amount of liabilities and owner’s equity, there must be some errors, omissions, or misclassifications. This is highly possible when you prepare it manually. For an error-free balance sheet with real-time updates, you can rely on accounting software like Financfy. You can also follow the templates provided above for a quick and easy preparation of your balance sheet.
FAQs: Balance Sheet Format in Bangladesh
1. Is a balance sheet mandatory in Bangladesh for all businesses?
Yes, a balance sheet is mandatory for all businesses in Bangladesh. It reflects the company’s assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity at a specific time.
2. How often should I prepare a balance sheet in BD?
As per the Companies Act in Bangladesh, businesses should prepare a balance sheet annually. But it’s better to prepare quarterly, especially when the business’s transactions are intensive.
3. Do I need an audited balance sheet for RJSC submission?
Yes, for Registrar of Joint Stock Company and Firm (RJSC) submission, you need an audited balance sheet. And it must be filed within the 30 days of the Annual General Meeting (AGM).
4. Which software can help create a Bangladeshi balance sheet?
Automated accounting software like Finacfy, FreshBooks, QuickBooks, AmarSolutions, etc., can help create a Bangladeshi balance sheet with zero errors.
5. What’s the difference between an income statement and a balance sheet?
An income statement is the summary of a company’s financial performance for a specific period of time. Meanwhile, the balance sheet is the financial position of the company at a specific point in time.



